Mechanical Modeler
Retrieving Mechanical Import Information using GUID Mechanism
Using CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative with GUID as authentication
AbstractThe Use Case creates a Mechanical Import It begins by copying a feature between two Part documents using the "Copy as Result with Link" option. This results in a Mechanical Import [ 1]. It further illustrates the steps involved to authorize retrieving information from this Mechanical Import. This includes generating a GUID [2] and specifying it to the copy process, so that it gets associated with the Mechanical Import. This GUID, finally authorizes us to seek all relevant information from the copied feature. |
What You Will Learn With This Use Case
This use case is intended to show you how to retrieve the relevant
information from the Mechanical Import and how to create and use the
GUID for copying as well as for retrieving
relevant information. For these
purpose Use case uses two interfaces:
- CATMmrInterPartCopy
- CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
CATMmrInterPartCopy: class services to copy a feature.
You will use this interface to copy a feature. You can read the referenced use case to learn more about this class [3].
CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative: The interface to retrieve the information from the copied feature. The information are
- The original feature
- The product instance ( if the copy is in assembly context)
SetImportApplicativeId and
SetApplicativeId methods uses GUID
associated with copied feature. SetImportApplicativeId sets
the GUID just prior to copying
operation and
SetApplicativeId sets the GUID after the copying operation for information retrieving.
[Top]
The CAAMmrApplicativeImport Use Case
CAAMmrApplicativeImport is a use case of the CAAMechanicalModeler.edu framework that illustrates MecModInterfaces framework capabilities.
[Top]
What Does CAAMmrApplicativeImport Do
The Use Case fundamentally copies a feature from a source Part to a target Part, both in Assembly context and out of it, and further retrieves relevant information from the copied feature. It operates on an Input Model as the one depicted in Fig. 1 below.
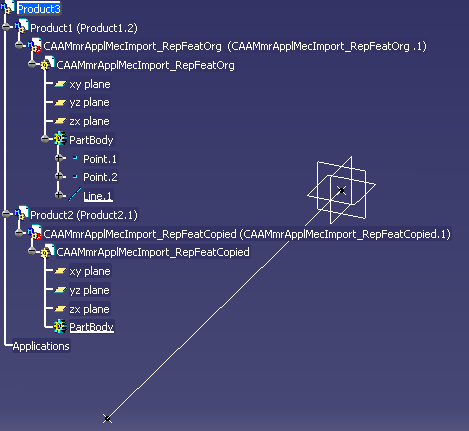 |
Suppose you want to copy the Line.1 feature then
at the end of the Use Case execution, the Line.1
feature from CAAMmrApplMecImport_RepFeatOrg
is copied within the target Part
CAAMmrApplMecImport_RepFeatCopied, in assembly context as
well as out of assembly context. Mechanical Import is the result of feature copy, it is a feature returned
by the Run method. It is also valid for Point, Line, Curve and Plane.
But take care, suppose you try to copy BodyPart, Geometrical Set, Sketch feature, the feature returned by the Run
method is not a Mechanical Import itself but the features beneath it are the
Mechanical Import, this is properly explained in the technical article[1].
Most importantly, the Use Case illustrates the failure to
retrieve the relevant information (source feature and Product Instance) from
the copied feature, if you do not have the proper authorization for this
retrieval. It further illustrates to us a mechanism to authorize
retrieval of data by associating the copied feature with a GUID (using the CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
Interface) during the copying process.
The creation of GUID is illustrated in step by
step section.
[Top]
How to Launch CAAMmrApplicativeImport
To launch CAAMmrApplicativeImport, you will need to set up the build time environment,
then compile CAAMmrApplicativeImport along with its prerequisites, set up the run time
environment, and then execute the use case [4].
To launch the use case execute the command:
mkrun -c "CAAMmrApplicativeImport
InputPath Feature"
where
$InstallRootDirectory\CAAMechanicalModeler.edu\InputData
Example:
mkrun -c "CAAMmrApplicativeImport
$InstallRootDirectory\CAAMechanicalModeler.edu\InputData Point.1"
[Top]
Where to Find the CAAMmrApplicativeImport Code
The CAAMmrApplicativeImport use case is located in the
CAAMmrApplicativeImport.m module of the
CAAMechanicalModeler.edu framework:
InstallRootDirectory\CAAMechanicalModeler.edu\CAAMmrApplicativeImport.m\ |
where InstallRootDirectory [4]
is the directory where the CAA CD-ROM
is installed.
[Top]
Step-by-Step
There are two logical parts in CAAMmrApplicativeImport, first part is
consist of generation of GUID and second part is a batch which consist
of operations like Copying feature with and without assembly context as
well as retrieving of information from the Mechanical Import.
Creating the GUID
- Generating the GUID
uuidgen is a command, generates the header file which contains
GUID. We
need to run this command on windows prompt and create the header file.
- Edit the header file
replace INTERFACENAME word by GUID CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport, and remove the comments /*.... */
#ifndef CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport_H #define CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport_H GUID CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport = {/* 7c7b3737-5358-0000-0280-020b3e000000 */0x7c7b3737, 0x5358, 0x0000, {0x02, 0x80, 0x02, 0x0b, 0x3e, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00} }; #endif
The CAAMmrUUIDForApplicativeImport.h
can be located in any *Interfaces directory, based on the scope within which
it is accessed by the client applications. Please note that the same
GUID can be associated with any number of Mechanical
Imports.
Second part is also divided in several logical steps:
- Make the Copy
- Set information relevant for feature copy
- Using GUID to be kept by the Mechanical Import
- Copy feature to target part
- Retrieve information from the copied feature using CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
- Reset the CATMmrInterPartCopy pointer
[Top]
Make the Copy
Retrieve the CATMmrInterPartCopy Interface pointer
The CreateMmiInterPartCopy method of CATMmiPubServicesAccess is used to creates a pointer on a
CATMmrInterPartCopy enabling to
copy geometry.
...
CATMmrInterPartCopy* pInterPartCopy = NULL;
rc = CATMmiPubServicesAccess::CreateMmiInterPartCopy(pInterPartCopy);
...
|
Set information relevant for feature copy
The process of actually copying a feature, is twofold. Initially we set the relevant information, essential for the copying operation. This is followed by the actual copy process.
The CreateMmiInterPartCopy Interface has a set of
APIs, illustrated in the code below, for setting these copy parameters.
...
CATBaseUnknown_var spTargetPart = spSpecObjectOnMechPartOfRepFeatCopied;
CATBoolean CopyWithLink = TRUE;
pInterPartCopy->SetObject(spFeatureToCopy);
pInterPartCopy->SetTarget(spTargetPart);
pInterPartCopy->SetProducts(spPLMProductOnInstChild1,spPLMProductOnInstChild2 );
pInterPartCopy->SetLinkMode(CopyWithLink) ;
...
|
SetObject and SetTarget are used to set the source object and target feature for
copying.
SetProducts is used to set the source and target
products context, it works only in case of copying in assembly context.
Here SetLinkMode (CopyWithLink is
TRUE) is used to Keep the link between source object and destination
object, to reflect the changes in geometry. CopyWithLink should
be TRUE as it is mandatory to create Mechanical Import.
Using GUID to be kept by the Mechanical Import
...
pInterPartCopy->SetImportApplicativeId(CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport);
...
|
SetImportApplicativeId uses
GUID and sets an applicative identifier on the created
Mechanical Import, this method must be called before the Run
method. The
application which produces the copied feature can expose one special
identifier which is GUID. This identifier get associated with copied
feature at the time of copying. And this association is done by
SetImportApplicativeId.
Copy feature to target part
...
CATISpecObject_var ResultCopyAssm ;
pInterPartCopy->Run(ResultCopyAssm );
...
|
After setting all related information like source,
target and other parameters in CATMmrInterPartCopy object (i.e.
pInterPartCopy in this example), its time to call Run method. This will compute
the copy according to the specified inputs and the result will return in
ResultCopyAssm.
[Top]
Retrieve information from the copied feature using CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
Retrieve the CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative*
type on the copied feature. The CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
Interface exposes CAA services to enable us retrieve
information of the source feature from the copied feature.
..
CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative *pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy = NULL ;
rc = ResultCopyAssm ->QueryInterface(IID_CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative,
(void**)&pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy);
...
|
Before we proceed to seek the relevant information from
the copied feature, it is mandatory that we specify the Applicative
Identifier (GUID), (associated with the Mechanical Import, in an earlier
step) to the retrieval mechanism.
The following extract of code, illustrates the failure to retrieve information, in the absence of proper authorization. Once proper authorization is set, the calls which retrieve the information return SUCCESS.
...
CATBaseUnknown_var spPointedElement1 ;
rc = pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy->GetPointedElement(spPointedElement1 );
if (SUCCEEDED(rc))//It should fail
return 1;
rc = pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy->SetApplicativeId(CAAMmrGUIDForApplicativeImport);
rc = pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy->GetPointedElement(spPointedElement1 );
...
|
GetPointedElement returns a
pointer to the pointed element. It may be a sub-element or a feature.
Before setting the applicativeId the GetPointedElement method
should fail.
SetApplicativeId is used to
set the applicative identifier. You have to give here the identifier of
the mechanical import. If you don't give the correct identifier, all
methods of this interface will fail.
After setting the ApplicativeId you will be authorized
to retrieve the information from the feature and this case your
GetPointedElement will work.
We now proceed to seek other relevant information from the copied feature.
...
CATBoolean LoadedPointedReference ;
rc = pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy->IsPointedElementLoaded(LoadedPointedReference);
CATBaseUnknown_var spSourceProductInstance1;
pIMecImportApplicativeOnResultCopy->GetSourceProduct(spSourceProductInstance1);
... |
IsPointedElementLoaded gives the loading
status of the pointed representation.
GetSourceProduct
retrieve the Product Instance aggregating the Part document of the
Source Feature. And the function will product instance in
spSourceProductInstance1, this happens only in case of
copy in assembly context. But in case of copy without assembly context
method should have to fail. In copying feature for without assembly
context you can only retrieve the original feature, no product instance.
[Top]
Reset the CATIMmiInterPartCopy pointer
After every confirmation of result we should have to
reset the CATMmrInterPartCopy pointer for next
copy.
...
pInterPartCopy->Reset();
...
|
[Top]
In Short
The Use Case creates a Mechanical Import, an end result
of copying a feature, with the Link mode set to
TRUE. A Mechanical Import implements the CATIMmiMechanicalImportApplicative
Interface, which
enables us to retrieve relevant information of the source feature from
its copied entity.
The process of actually retrieving this information
needs proper authorization. The Use Case illustrates the failure to
retrieve information, in the absence of proper authorization and details
the steps involved in generating a GUID (Applicative ID) and specifying
it to the copying process, so that it associates it with the Mechanical
Import.
Finally, this GUID is specified to the retrieving
mechanism, which authorizes us to retrieve the source feature, its
aggregating Product Instance and its load status.
[Top]
References
| [1] | Managing Applicative Mechanical Imports |
| [2] | About Globally Unique Identifiers |
| [3] | Copying Mechanical Features |
| [4] | Building and Launching a CAA V5 Use Case |
[Top]
History
| Version: 1 [July 2007] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2007, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.