3D PLM Enterprise Architecture |
Middleware Abstraction |
Creating a Backbone Data MessageCreating a message that conveys data |
| Use Case | ||
AbstractThis article shows how to create a backbone data message component, that is, a message component that conveys data. This message component can then be used to make two processes or applications communicate. |
This use case shows you how to create a backbone data message, that is, that conveys data. This use case shows how to create a component that derives from the base message component CATBBMessage, and that implements, in the component main class, the CATIStreamMsg interface with data to stream and unstream. In addition, it shows you how to implement CATICreateInstance using a code extension class to enable clients to instantiate the message component.
[Top]
CAASysBBMessage is a use case of the CAASystem.edu framework that illustrates the System framework capabilities.
[Top]
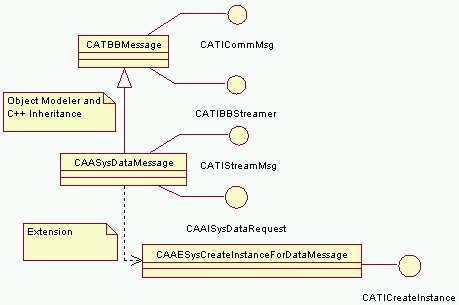
The message component is named CAASysDataMessage and derives from the CATBBMessage component. CAASysDataMessage implements the CATIStreamMsg and CATICreateInstance interfaces. It also inherits the implementation of the CATICommMsg and CATIBBStreamer interfaces from CATBBMessage. CATICreateInstance is implemented using a code extension class.

CATIStreamMsg is implemented to convey the data that define a circle. To get and set this data, CAASysDataMessage also implements the CAAISysDataRequest interface. This data is:
| The circle radius | float |
| The circle number | int |
| The circle color | char * |
| The circle sags | array of floats |
The CAASysBBMessage use case also includes another backbone message component that doesn't convey any data [1].
[Top]
CAASysBBMessage is launched by other backbone use cases [2][3], but you need to create the CAASysBBMessage shared library or DLL. To do this, you will need to set up the build time environment, and compile CAASysBBMessage along with its prerequisites [4].
[Top]
The CAASysBBMessage use case is made of several classes located in the CAASysBBMessage.m module of the CAASystem.edu framework:
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory\CAASystem.edu\CAASysBBMessage.m\ |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory/CAASystem.edu/CAASysBBMessage.m/ |
where InstallRootDirectory is the directory where the CAA CD-ROM
is installed.
[Top]
To create a backbone data message, there are four main steps:
| # | Step | Where |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creating the message component main class | LocalInterfaces\CAASysDataMessage.h src\CAASysDataMessage.cpp |
| 2 | Implementing CATIStreamMsg | LocalInterfaces\CAASysDataMessage.h src\CAASysDataMessage.cpp |
| 3 | Implementing CAAISysDataRequest | LocalInterfaces\CAASysDataMessage.h src\CAASysDataMessage.cpp |
| 4 | Creating the message component factory | LocalInterfaces\CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage.h src\CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage.cpp |
| 5 | Updating the interface dictionary | CNext\code\dictionary\CAASystem.edu.dico |
[Top]
A backbone message is a component that is made up of a main class. Its header file is as follows:
#include "CATBBMessage.h"
class CAASysDataMessage : public CATBBMessage
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAASysDataMessage();
virtual ~CAASysDataMessage();
// CATIStreamMsg interface methods
virtual HRESULT StreamData (void **oBuffer, uint32 *oLen);
virtual HRESULT UnstreamData (void *iBuffer, uint32 iLen);
virtual HRESULT FreeStreamData(void *iBuffer, uint32 iLen);
virtual HRESULT SetMessageSpecifications();
// CAAISysDataRequest interface methods
virtual HRESULT SetData(const float iRadiusOfCircle,
const int iNbOfCircle,
char * iColorOfCircle,
float * iSagOfCircle);
virtual HRESULT GetData(float & oRadiusOfCircle,
int & oNbOfCircle,
char ** oColorOfCircle,
float ** oSagOfCircle);
private:
CAASysDataMessage(const CAASysDataMessage &iObjectToCopy);
private:
float _RadiusOfCircle;
int _NbOfCircle;
char * _ColorOfCircle;
float _SagOfCircle[3];
};
|
The CAASysDataMessage class belongs to a component, thanks to the CATDeclareClass
macro. It C++ derives from CATBBMessage, and implements CATIStreamMsg,
whose four methods are declared. In addition, it implements an application
interface to retrieve and set the data of the circle component it is intended to
convey. Note that the copy constructor is set as private, and is not implemented
in the source file. This prevents the compiler from creating the copy
constructor as public without you know. The circle component data are declared
as private data members.
The source file of the backbone data message component main class begins as follows:
#include "CAASysDataMessage.h"
#include <CATErrorDef.h> // for the SUCCEEDED macro
#include "CATIBBStreamer.h" // To stream
#include "CATICommMsg.h"
#include "TIE_CATIStreamMsg.h"
TIE_CATIStreamMsg(CAASysDataMessage);
#include "TIE_CAAISysDataRequest.h"
TIE_CAAISysDataRequest(CAASysDataMessage);
CATImplementClass(CAASysDataMessage, Implementation, CATBBMessage, CATNull);
CAASysDataMessage::CAASysDataMessage()
: _ColorOfCircle(NULL),_NbOfCircle(0),_RadiusOfCircle(0.f)
{
_SagOfCircle[0] = 0.0f;
_SagOfCircle[1] = 0.0f;
_SagOfCircle[2] = 0.0f;
}
CAASysDataMessage::~CAASysDataMessage()
{
if ( NULL != _ColorOfCircle )
{
delete [] _ColorOfCircle;
_ColorOfCircle = NULL;
}
}
...
|
The CAASysDataMessage class states that it implements the CATIStreamMsg
and CAAISysDataRequest interfaces thanks to the TIE_CATIStreamMsg
and TIE_CAAISysDataRequest macros respectively. The CATImplementClass
macro declares that the CAASysDataMessage class is a component main class
thanks the Implementation keyword, and that the component
OM-derives [5] from CATBBMessage. Any component
main class declared as an Implementation must C++-derive and
OM-derive from the same class. The constructor and the destructor respectively
initializes and deletes the data members.
[Top]
CATIStreamMsg is the interface dedicated to streaming and unstreaming the data that the message conveys. Four methods must be implemented:
StreamData |
Streams a backbone message |
UnstreamData |
Unstreams a backbone message |
FreeStreamData |
Frees the backbone message streaming buffer |
SetMessageSpecifications |
Sets backbone message class name and options |
These methods are implemented for the circle object.
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::StreamData(void **oBuffer, uint32 *oLen)
{
CATIBBStreamer * pICATIBBStreamer = NULL ;
HRESULT rc = QueryInterface(IID_CATIBBStreamer, (void**)&pICATIBBStreamer);
if ( SUCCEEDED(rc) )
{
pICATIBBStreamer->BeginStream();
pICATIBBStreamer->StreamFloat(_RadiusOfCircle);
pICATIBBStreamer->StreamInt(_NbOfCircle);
pICATIBBStreamer->StreamString(_ColorOfCircle);
pICATIBBStreamer->StreamFixedFloatArray(_SagOfCircle,3);
int Len ;
*oBuffer = pICATIBBStreamer->EndStream(&Len);
*oLen = Len ;
pICATIBBStreamer->Release();
pICATIBBStreamer = NULL;
}
return rc;
}
|
The data to stream for the circle is made up of simple types only. An
easy way of implementing such data streaming is to retrieve a pointer to the
CATIBBStreamer interface that the component implements thanks to the
inheritance of CATBBMessage. CATIBBStreamer provides a set of
streaming methods for simple types that just need to be called. First,
initialize the streaming operation using BeginStream, and then
stream the data:
| The circle radius | float | StreamFloat |
| The circle number | int | StreamInt |
| The circle color | char * | StreamString |
| The circle sags | array of floats | StreamFixedFloatArray |
Then, close the streaming operation using EndStream, release
the CATIBBStreamer pointer and set it to NULL, and
that's done.
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::UnstreamData(void *iBuffer, uint32 iLen)
{
CATIBBStreamer * pICATIBBStreamer = NULL;
HRESULT rc = QueryInterface(IID_CATIBBStreamer, (void**)&pICATIBBStreamer);
if ( SUCCEEDED(rc) )
{
pICATIBBStreamer->BeginUnstream(iBuffer,iLen);
pICATIBBStreamer->UnstreamFloat(&_RadiusOfCircle);
pICATIBBStreamer->UnstreamInt(&_NbOfCircle);
int Len;
pICATIBBStreamer->UnstreamNeededStringLength(&Len);
_ColorOfCircle = new char [Len];
pICATIBBStreamer->UnstreamString(_ColorOfCircle);
pICATIBBStreamer->UnstreamFixedFloatArray(_SagOfCircle, 3);
rc = pICATIBBStreamer->EndUnstream();
pICATIBBStreamer->Release();
pICATIBBStreamer = NULL;
}
return rc;
}
...
|
Unstreaming the circle data streamed is also performed by retrieving a
pointer to the CATIBBStreamer interface. CATIBBStreamer
provides a set of unstreaming methods for simple types that just need to be
called. First, initialize the unstreaming operation using BeginUnstream,
and then unstream the data in the same order than when streaming:
| The circle radius | float | UnstreamFloat |
| The circle number | int | UnstreamInt |
| The circle color | char * | UnstreamString |
| The circle sags | array of floats | UnstreamFixedFloatArray |
Note that prior to unstream a character string, you should retrieve its
length thanks to UnstreamNeededStringLength, and allocate the
character string. When all data is unstreamed, close the unstreaming
operation using EndUnstream, release the CATIBBStreamer
pointer and set it to NULL, and that's done.
...
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::FreeStreamData(void *iBuffer, uint32 iLen)
{
CATIBBStreamer * pICATIBBStreamer = NULL;
HRESULT rc = QueryInterface(IID_CATIBBStreamer,(void**)&pICATIBBStreamer);
if ( SUCCEEDED(rc) )
{
pICATIBBStreamer->ResetStreamData();
pICATIBBStreamer->Release();
pICATIBBStreamer = NULL ;
}
return rc ;
}
...
|
To free the stream buffer when only simple types are streamed and
unstreamed, simply retrieve a pointer to the CATIBBStreamer interface
and call ResetStreamData.
...
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::SetMessageSpecifications()
{
HRESULT rc = E_FAIL;
CATICommMsg * pICommMsg = NULL ;
rc = QueryInterface(IID_CATICommMsg, (void**)&pICommMsg);
if ( SUCCEEDED(rc) )
{
CATMessageClass MessageClassName= "CAASysDataMessage";
rc = pICommMsg->SetMessageClass(MessageClassName);
pICommMsg->Release();
pICommMsg = NULL ;
rc = S_OK;
}
return rc;
}
|
The message specifications that must be set are at least the name of the
message component main class. This is to enable the message component to be
instantiated at unstreaming time. This is done by retrieving a pointer to
the CATICommMsg interface that the component implements thanks to the
inheritance of CATBBMessage. Simply call the SetMessageClass
with the message class name as argument.
[Top]
CAAISysDataRequest is an interface the component should implement to
enable the data to be set and retrieved, and is therefore component dependent. CAAISysDataRequest
has two methods, SetData and GetData.
SetData
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::SetData(const float iRadiusOfCircle,
const int iNbOfCircle,
char *iColorOfCircle,
float *iSagOfCircle)
{
_RadiusOfCircle = iRadiusOfCircle;
_NbOfCircle = iNbOfCircle;
if ( NULL != iColorOfCircle )
{
_ColorOfCircle = new char [strlen(iColorOfCircle)+1];
strcpy(_ColorOfCircle,iColorOfCircle);
}
_SagOfCircle[0] = iSagOfCircle[0];
_SagOfCircle[1] = iSagOfCircle[1];
_SagOfCircle[2] = iSagOfCircle[2];
return S_OK;
}
|
SetData is used by the message sender when the message is
created to feed the message with the circle data [3].
GetData
HRESULT CAASysDataMessage::GetData(float & oRadiusOfCircle,
int & oNbOfCircle,
char ** oColorOfCircle,
float ** oSagOfCircle)
{
HRESULT rc = E_FAIL;
if ( (NULL != oSagOfCircle) && ( NULL != oColorOfCircle) )
{
oRadiusOfCircle = _RadiusOfCircle;
oNbOfCircle = _NbOfCircle;
if ( NULL != _ColorOfCircle )
{
*oColorOfCircle = new char [strlen(_ColorOfCircle)+1];
strcpy(*oColorOfCircle,_ColorOfCircle);
}
else
{
*oColorOfCircle = NULL;
}
*oSagOfCircle = new float[3] ;
(*oSagOfCircle)[0] = _SagOfCircle[0];
(*oSagOfCircle)[1] = _SagOfCircle[1];
(*oSagOfCircle)[2] = _SagOfCircle[2];
rc = S_OK;
}
return rc;
}
|
GetData is used by the message receiver when the message is
received to get the circle data from the message [3].
[Top]
As any component, a backbone message should provide a means for any client application to instantiate it [6]. This is made possible by making the component implement CATICreateInstance using a code extension class. Below is the header file of this class.
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" //Needed to derive from CATBaseUnknown
class CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage : public CATBaseUnknown
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage();
virtual ~CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage();
// CATICreateInstance method
virtual HRESULT __stdcall CreateInstance(void **oppv);
private:
CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage(const CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage &iObjectToCopy);
};
|
The CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage class belongs to a component,
thanks to the CATDeclareClass macro. It C++ derives from CATBaseUnknown,
and implements CATICreateInstance, whose unique method CreateInstance
is declared. Note that the copy constructor is set as private, and is not
implemented in the source file. This prevents the compiler from creating the
copy constructor as public without you know.
The source file of this code extension class is as follows:
#include "CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage.h"
#include "CAASysDataMessage.h"
#include "TIE_CATICreateInstance.h"
TIE_CATICreateInstance(CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage);
CATImplementClass(CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage,
CodeExtension,
CATBaseUnknown,
CAASysDataMessage);
CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage::CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage() {}
CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage::~CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage() {}
HRESULT __stdcall CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage::CreateInstance(void ** oppv)
{
CAASysDataMessage * pt = new CAASysDataMessage();
if (!pt) return(E_OUTOFMEMORY);
*oppv = (void *)pt;
return(S_OK);
}
|
The CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage class states that it
implements the CATICreateInstance interface thanks to the TIE_CATICreateInstance
macro. The CATImplementClass macro declares that the CAAESysCreateInstanceForDataMessage
class is a code extension class, thanks to the CodeExtension
keyword, and that it extends the component whose main class is CAASysDataMessage.
The third parameter must always be set to CATBaseUnknown, makes no sense,
and is unused for extensions. The CreateInstance method
instantiates and returns the component main class.
[Top]
The interface dictionary is updated as follows.
CAASysDataMessage CATIStreamMsg libCAASysBBMessage CAASysDataMessage CATICreateInstance libCAASysBBMessage CAASysDataMessage CAAISysDataRequest libCAASysBBMessage |
The interface dictionary is a file whose name is the framework name suffixed by dico, such as CAASystem.edu.dico, and that you should create or update in the framework CNext\code\dictionary directory. The interface dictionary declares that the CAASysDataMsg component implements CATIStreamMsg, CATICreateInstance, and CAAISysDataRequest, and that the shared library or DLL to load to query pointers to these interfaces is libCAASysBBMessage.
[Top]
This use case has shown how to create a backbone data message that can be
used to communicate between two applications. As any backbone message, the
message is made up of a component that derives from the supplied CATBBMessage
component, that itself implements CATIStreamMsg and CATICreateInstance
interfaces, and that inherits from CATBBMessage the implementation of the
CATIBBStreamer and CATICommMsg interfaces. Such a message that
conveys data of simple types can use the streaming and unstreaming methods
provided by the CATIBBStreamer implementation of CATBBMessage.
Data must be streamed and unstreamed in the same order. The message is now ready
to be used by applications [3].
[Top]
| Version: 1 [Jul 2000] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2000, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.