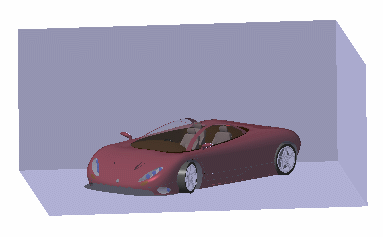
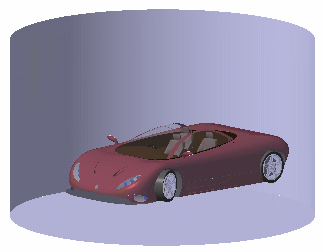
An environment is a simplified simulation of a landscape surrounding your model and directly reflected by your model. It is an efficient way to get a very quick feedback of the illumination behavior of your model and check its integration in its final environment. For example, placing neon lights as a 3D-texture on the ceiling will be used for car body design, while referring to a picture of a Norvegian forest for the walls will produce an impressive marketing image of a newly designed chainsaw.
-
Click Create Box Environment
 to create an environment with a rectangular shape (to represent a room
for example).
to create an environment with a rectangular shape (to represent a room
for example). -
Zoom out then click anywhere in the geometry area to deselect the environment.
-
Position your pointer over the edges then use the green segments
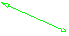 displayed to resize the
environment walls:
displayed to resize the
environment walls:- drag a segment to resize the walls according to the edges
- press Shift and drag a segment to resize the walls according to the center.
-
Right-click the environment in the specification tree then select Properties (or press Alt+Enter). The Properties dialog box is displayed.
-
The Dimensions tab enables you to define the environment size. In our example, specify the Length, Width and Height of the walls in millimeters:
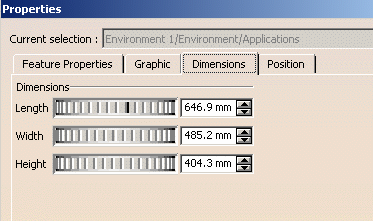
-
Click the Position tab to interactively define:
-
the environment translation from the origin along the X, Y or Z axis
-
the environment translation along the X, Y, or Z Axis.
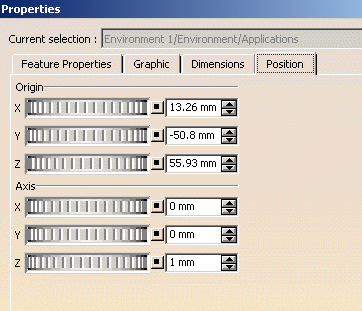
-
The Feature Properties tab provides general information on the currently selected environment, e.g. its name, its creation date, etc.
![]()